More than just another wellness fad, h*mp is a botanical powerhouse backed by science. For centuries, healers have tapped into its benefits, but modern research is now proving what ancient wisdom always knew — h*mp has the potential to restore balance, ease stress and support overall vitality.
At the heart of h*mp’s magic is the endocannabinoid system (ECS) — your body’s built-in regulator for mood, inflammation and more. It’s a sophisticated network you might not even know you have. When nourished with the right compounds, like those found in h*mp products, the ECS helps keep everything in check.
This guide will break down the science behind h*mp’s game-changing effects and answer common questions like “What are h*mp gummies used for?” or “How do h*mp products fit into a holistic wellness routine?”.
How h*mp interacts with our body
The Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signalling system identified in the early 1990s by researchers exploring THC, a well-known cannabinoid. These natural compounds, found in cannabis, interact with the ECS in ways scientists are still working to fully understand. But so far, we know it plays a role in regulating a range of functions and processes, including sleep, mood, appetite, memory, reproduction and fertility.
- The ECS exists and is active in your body even if you do not use cannabis.
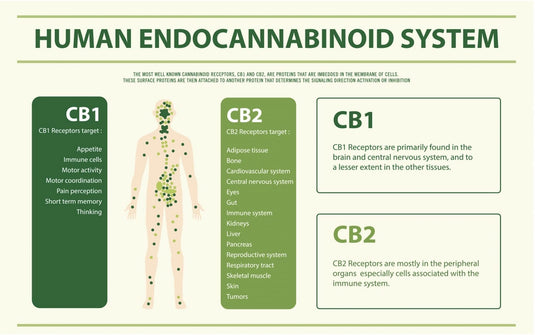
- The ECS involves three core components: endocannabinoids, receptors and enzymes.
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids, also called endogenous cannabinoids, are naturally occurring molecules. They are similar to cannabinoids, except the body produces them. Experts have identified two key endocannabinoids so far: anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG). These compounds support essential functions and help keep the body’s systems running efficiently. Since they are produced on demand, their levels fluctuate, making it difficult to determine a typical baseline for each.
Endocannabinoid receptors
These receptors are found throughout your body. Endocannabinoids bind to them in order to signal that the ECS needs to take action. There are two main endocannabinoid receptors:
- CB1 receptors, which are mostly found in the central nervous system.
- CB2 receptors, which are mostly found in your peripheral nervous system, especially immune cells.
Endocannabinoids can bind to either receptor. The effects depend on where the receptor is located and which endocannabinoid it binds to. For example, endocannabinoids might target CB1 receptors in a spinal nerve to relieve pain. Others might bind to a CB2 receptor in your immune cells to signal that your body’s experiencing inflammation, a common sign of autoimmune disorders.
Phytocannabinoids are a diverse group of naturally occurring chemical compounds found in the Cannabis plant.
H*mp oil — nature’s nutrient-rich remedy
H*mp oil has gained widespread recognition as a natural wellness staple. Its advocates claim anecdotal evidence for curative properties ranging from improving acne to treating cancer to slowing the progression of heart disease and Alzheimer’s.
Some of these claims are yet to be proven by clinical research.
However, data suggests that h*mp oil may help certain health issues, such as inflammation and skin conditions. This is primarily because of its essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), including omega-3s and omega-6s.
Fatty acids, which we obtain from food, are vital for the normal operation of all body systems. H*mp oil contains omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids in a ratio of 3:1, which is proposed to be the ideal ratio.
H*mp oil and inflammation
H*mp oil is also a rich source of gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), a type of omega-6 fatty acid. Studies suggest that adding omega-3s, such as those found in h*mp oil, to your diet can reduce inflammation. Inflammation can contribute to diseases such as cancer and heart disease.
H*mp oil and skin disorders
Research indicates that the omega-3s and omega-6s in h*mp oil may be effective in treating a number of skin conditions, including:
- Acne — A 2014 study concludes that h*mp oil (nonpsychotropic phytocannabinoid cannabidiol) is a potent and potentially universal anti-acne treatment. The study states that clinical trials are needed to fine-tune ways to best take advantage of its benefits.
- Eczema — A 20-week study in 2005 concludes that dietary h*mp oil resulted in the improvement of eczema symptoms.
- Psoriasis — A 2015 study indicates that omega-3 fatty acids, as a nutritional supplement, may be beneficial in the treatment of psoriasis. The study suggests they should be used in combination with topical vitamin D, UVB phototherapy and oral retinoids.
- Lichen planus — A 2014 article indicates that h*mp oil is useful for the treatment of the inflammatory skin condition lichen planus. The 2014 article also suggests that h*mp oil can contribute to stronger skin that is more resistant to viral, bacterial, and fungal infections.
H*mp oil, PMS and menopause
A 2011 study suggests that the physical or emotional symptoms associated with premenstrual syndrome are potentially caused by sensitivity to the hormone prolactin that may be related to low prostaglandin E1 (PGE1).
H*mp oil’s gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) assists in the production of PGE1. The study showed that women with PMS who took 1 gram of fatty acids that included 210 mg of GLA experienced a notable decrease in symptoms.
H*mp oils as an antibacterial agent
A 2017 study of h*mp oil’s antibacterial properties inhibited the activity of various types of bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus.
Staphylococcus aureus is a dangerous bacteria that can cause skin infections, pneumonia and infections of the skin, bone and heart valves.
So, in conclusion, h*mp oil has an amazing range of health benefits that can assist you in living your best life.
H*mp gummies — where convenience meets satisfaction
H*mp products come in many forms, but few are as popular and accessible as gummies. While tinctures and oils have long been used for their fast absorption, h*mp gummies are quickly becoming the preferred choice for those looking for a convenient, enjoyable way to experience h*mp’s benefits.
What are h*mp gummies used for?
Much like h*mp oil, gummies are used for stress relief, relaxation, better sleep and overall wellness. Here are a few reasons why they’ve become popular in recent years:
- No mess, no measuring — Unlike oils, which require a dropper, gummies are ready to go whenever you need them.
- Tastier alternative — H*mp oil’s natural, earthy taste isn’t for everyone. Gummies provide a delicious option without sacrificing effectiveness.
- Perfect for beginners and experienced users — Whether you’re new to h*mp or already a fan, gummies offer an approachable, enjoyable way to incorporate h*mp into your routine.
- Tailored formulations — Many h*mp gummies are enhanced with chamomile or vitamins, making them multi-functional wellness tools.
Unlock the power of h*mp for a better you
H*mp has come a long way from being misunderstood to becoming a trusted, science-backed solution for wellness. As research continues to reveal its far-reaching benefits, one thing is clear: h*mp is a natural ally for those seeking relief, relaxation and a healthier lifestyle.
At Rapha Herbals, we craft premium, science-driven formulations designed for real results. Our gummies are made with high-quality h*mp extract, blended with an herbal form of serotonin and dopamine, to support a happier, healthier you. Plus, our third-party verification and patented CO2 extraction process ensure purity, potency and effectiveness in every bite.
If you’ve been intrigued by what h*mp gummies are used for and how they can enhance your wellness routine, shop online today. Please feel free to reach out to us for any questions or concerns.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before using h*mp products, especially if you are pregnant, nursing, taking medication or have a medical condition.